Common Stock What Is It, Vs Preferred Stock, Formula
You can get these numbers if you dive the frequency for each delivery time with the total cases, in our case, the last ten orders. When customers know they can count on your business to provide the products they need, even during peak demand or supply chain disruptions, their trust in your brand increases. So, having enough safety stock will prevent you from these stockouts and ensure you meet the demand consistently, thus protecting your revenue.
How to Calculate Cumulative Dividends Per Share
Common Stockholders are the company’s owners; they earn voting rights and are eligible for dividends. It’s also important to mention that some, but not all, cumulative preferred stocks have additional provisions to compensate shareholders if preferred dividends are suspended. For example, some preferred stocks require accumulated dividends to be repaid with interest. In Goodrich Petroleum’s case, if dividends remain unpaid for six quarters, the preferred shareholders become entitled to two seats on the company’s board. One series also increases its dividend rate by 1% per year until all accumulated and unpaid dividends are paid in full. Another useful metric for valuing a stock or company is the price-to-book ratio.
Standard Deviation Safety Stock Formula
This says that if any dividend payments have been skipped, they must be paid out to preferred shareholders before common shareholders are paid any current dividends. Cumulative dividend provisions are intended to give preferred shareholders confidence that they’ll receive the stated return on their investments. Common stock represents a residual ownership stake in a company, the right to claim any other corporate assets after all other financial obligations have been met. Assets include what the company owns or is owed, such as its property, equipment, cash reserves, and accounts receivable. On the other side of the ledger are liabilities, which are what the company owes. If a company is healthy, the total assets will be larger than the total liabilities.
Is common stock an asset on a balance sheet?
The market value per share is a company’s current stock price, and it reflects a value that market participants are willing to pay for its common share. The book value per share is calculated using historical costs, but the market value per share is a forward-looking metric that takes into account a company’s earning power in the future. With increases in a company’s estimated profitability, expected growth, and safety of its business, the market value per share grows higher. Significant differences between the book value per share and the market value per share arise due to the ways in which accounting principles classify certain transactions. While you have a lot of risk if a company goes bankrupt, common stocks offer high returns on investment if a company does well. Common stock tends to offer higher potential returns, but more volatility.
What is the difference between Common Stock and preferred stock?
- For instance, consider a company’s brand value, which is built through a series of marketing campaigns.
- Investing in common stock means you’re putting your money into a part of the company’s journey.
- This certificate is known as a stock certificate, capital stock, or stock.
- A company’s GAAP earnings are the amount of profit it generates on an unadjusted basis, meaning without regard for one-off or unusual events such as business unit purchases or tax incentives received.
Gordon Scott has been an active investor and technical analyst or 20+ years. In 2021, the share repurchases are assumed to be $5,000, which will be subtracted from the beginning balance. As for the “Treasury Stock” line item, the roll-forward calculation consists of one single outflow – the repurchases made in the current period. Earlier, we were provided with the beginning of period balance of $500,000. But an important distinction is that the decline in equity value occurs due to the “book value of equity”, rather than the market value. However, the issuance price of equity typically exceeds the par value, often by a substantial margin.

Selling preferred stock, like any other shares, lets a company raise money by selling a stake in the business. A company may do this to raise capital for business expansion, debt repayment, or to invest in new projects. Preferred stocks are less dilutive of company ownership since they do not come with voting rights. They offer the issuing firm other benefits, not least because being less volatile makes them appeal to different investors. The fixed dividends also stabilize the company’s balance sheet, making it more attractive to additional investors. Another reason is that, for some companies, the cost of issuing preferred stock is lower than issuing bonds.
Aside from metrics like the P/E ratio that are quantitatively computed, investors should consider companies’ qualitative strengths and weaknesses when gauging a stock’s value. A company’s price-to-book ratio is only marginally useful for evaluating companies, like software tech companies, that have asset-light business models. This metric is more relevant for evaluating asset-heavy businesses, such as banks and other financial institutions.
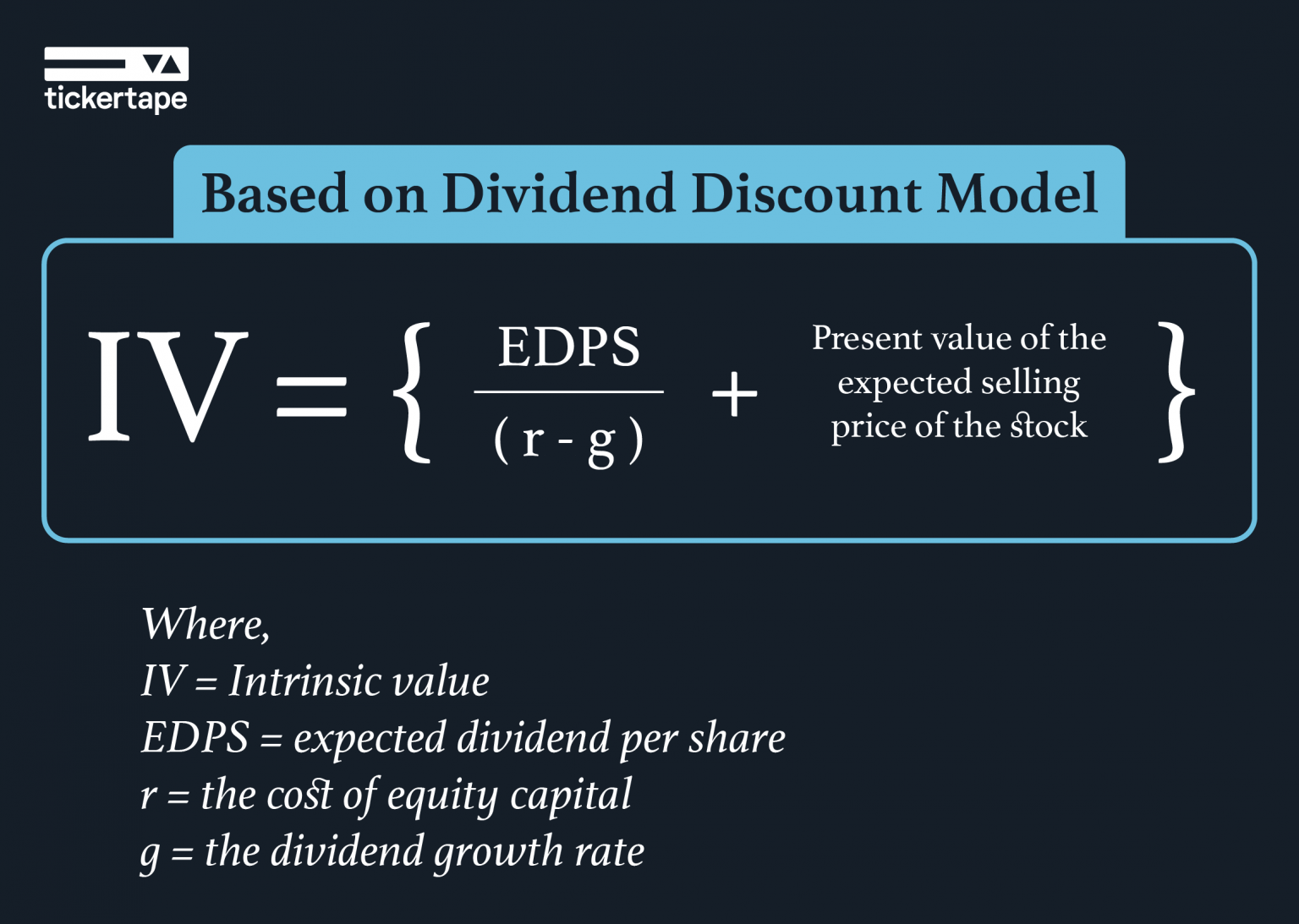
A P/E ratio that is good for one investor may not be enticing to another. P/E ratios can be viewed differently by different investors depending on their investment objectives, which may be more strongly oriented toward value or growth. A stock’s intrinsic value, rooted cloud computing in its business fundamentals, is not always the same as its current market price — although some people believe otherwise. Investors assign values to stocks because it helps them decide if they want to buy them, but there is not just one way to value a stock.

No Comments